
When the company pays the amount owed, accounts payable will decrease and cash will decrease. Some of a company’s assets are cash or things that can be converted to cash quickly. This gives assets priority when being classified on a balance sheet, since converting assets to cash may be a priority with lenders or potential buyers. The ability to convert assets to cash is called liquidity and it’s measured roughly in units of time. Those assets that convert quickly into Bookkeeping vs. Accounting cash, usually within one year of the balance sheet’s creation, are called current assets. Last on the balance sheet is the goodwill, which could be realized only at the time of sale or any other business restructuring.
- A current asset whose ending balance should report the cost of a merchandiser’s products awaiting to be sold.
- Its liquidity depends on the speed in which the inventory can be converted to cash.
- US GAAP uses the title ‘Balance Sheet’, while IFRS uses the title ‘Statement of Financial Position’.
- Money owed to a business by its customers for goods and services provided makes up accounts receivable.
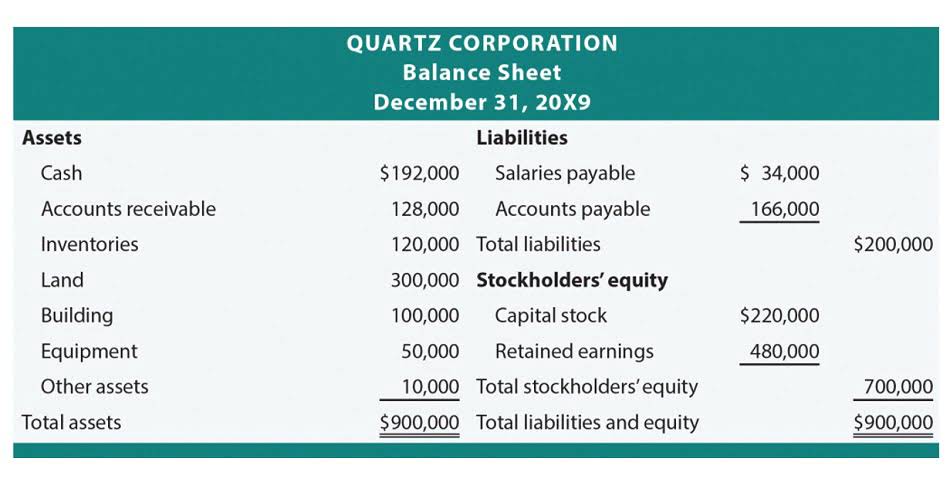
- A sample presentation of current assets is highlighted in the following balance sheet exhibit.
- Some companies use a business credit card to pay for the goods and services it receives.
Inventory turnover ratio
- A company’s order of liquidity is an important factor to consider when assessing its financial health.
- A liquid asset means any asset that is easy and quick to convert into cash without losing its market value.
- In other words, it is the company’s ability to convert its current assets to cash so that the current liabilities can be paid when they come due.
- It is also possible that the company paying with the business credit card will receive a cash rebate of 2% from the credit card company.
- In some cases, inventory may be resold quickly, so its place in the order of liquidity may vary by company.
The balance sheet is a part of a financial statement that presents the company’s assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity at a particular point in time, thereby providing insights into an entity’s financial position. Assets are listed in the balance sheet in order of their liquidity, where cash is listed at the top as it’s already liquid. The next on the list are marketable securities like stocks and bonds, which can be sold in the market in unearned revenue a few days; generally, the next day can be liquidated. The Quick Ratio, also known as the acid-test ratio, is a liquidity ratio used to measure a company’s ability to meet short-term financial liabilities. The quick ratio uses assets that can be reasonably converted to cash within 90 days.

The 10 Best Accounting Software Solutions for Educational Institutions
Short term liabilities like creditors, bank overdraft are matched with assets which are more liquid, while long term liabilities are matched with lesser liquid assets. Long-term liabilities come due more than one year after the date of the balance sheet. They include bank loans (such as Delicious Desserts’ $10,000 loan for bakery equipment), mortgages on buildings, and the company’s bonds sold to others.

Current Asset Presentation in the Balance Sheet
The answers may lead to an urgent need for an immediate reduction in expenses lest the company is forced to stop operating. Eliminating operating losses is also important for ongoing relationships with lenders, suppliers, customers, employees, owners and more. People within a company will have access to more current amounts and more detailed information that can be sorted, reviewed and analyzed. For example, if a company has current assets of $90,000 and its current liabilities are $80,000, the company has working capital of $10,000. Lenders and investors closely monitor current liabilities because they compete with current assets for cash.

Current Assets: Formula & Examples for 2025
Current assets are all assets that a company expects to convert to cash within one year. A company’s assets on its balance sheet are split into two categories – current and non-current (long-term or capital assets). Current assets are those assets that are easily converted into cash within a year or are expected to be used up within the year.
Understanding Financial Ratios That Use Current Assets
- The terms which indicate when payment is due for sales made on account (or credit).
- For reporting the financial health of a business, few reports are as essential as the balance sheet.
- They are usually presented in order of liquidity on the balance sheet and include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivables, inventory, prepaid, and other short-term assets.
- Order of liquidity is a financial concept that refers to the sequence in which assets are expected to be converted into cash or how quickly a liability is to be paid off.
- A company with $100,000 of current assets and $100,000 of current liabilities has no working capital.
This means the amount is due in 30 days; however, if the amount is paid in 10 days a discount of 2% will be permitted. Liabilities also include amounts received in advance for a future sale or for a future service to be performed. You can also think of the positive amounts as being positive, good, or favorable for a company’s liquidity. Negative amounts can be thought of as not good or unfavorable for a company’s liquidity. This calculation shows that the company’s inventory “turned over” on average 3 times during the year. Other factors include the credit terms that are allowed by the company’s suppliers, the company’s profitability and growth rate, the time required to complete a customer’s order, and more.
In addition, the customer may receive a 2% cash rebate from the credit card company. Cash includes a company’s currency, coins, petty cash fund, general checking account, payroll checking account, money received from customers but not yet deposited, etc. Sustainable footwear and apparel retailer Allbirds (BIRD) reported total current assets of $130.6 million for its 2024 fiscal year. Current assets appear at the top of the balance sheet, before any non-current assets. A sample presentation of current assets is highlighted in the following balance sheet exhibit.

Inventory turnover ratio and days’ sales for each item in inventory
There are three Types of Inventory – order of liquidity Raw material inventory, work in progress inventory, and finished goods inventory. Paul Mladjenovic is a financial, business, and investment educator and national speaker with 40-plus years of experience. He has authored numerous Dummies guides, including the bestselling Stock Investing For Dummies, Currency Trading For Dummies, Investing in Gold & Silver For Dummies, High-Level Investing For Dummies, and others.